3D Rendering: From Wireframes to AI-Powered Photorealism
3D rendering has revolutionized various industries, from entertainment and gaming to architecture and product design. This comprehensive guide explores the journey of 3D rendering technology, its current state, and the exciting future ahead with AI integration.
Understanding 3D Rendering
3D rendering transforms 3D wireframe models into stunning 2D images with photorealistic qualities. This complex process represents the culmination of the 3D production pipeline, occurring after modeling and animation stages are complete.
Core Elements of the Rendering Process
| Component | Description | Technical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | 3D mesh structures and polygonal shapes | Polygon count, topology, edge flow |
| Materials | Surface characteristics and properties | PBR workflows, shader networks, BSDF models |
| Lighting | Scene illumination sources | Global illumination, HDRIs, ray tracing |
| Textures | Surface detail mapping | UV mapping, normal maps, displacement |
| Camera | Scene composition and framing | Focal length, DOF, motion blur |
As noted by industry veteran John Carmack: "The rendering equation doesn't care whether you are doing offline or real-time rendering; the physics is the same."
Historical Evolution
1960s-1970s: The Dawn of Computer Graphics
| Year | Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1963 | Sketchpad by Ivan Sutherland | First interactive computer graphics program |
| 1968 | First 3D wireframe models | Enabled basic object visualization |
| 1972 | Utah teapot model | Became standard 3D test model |
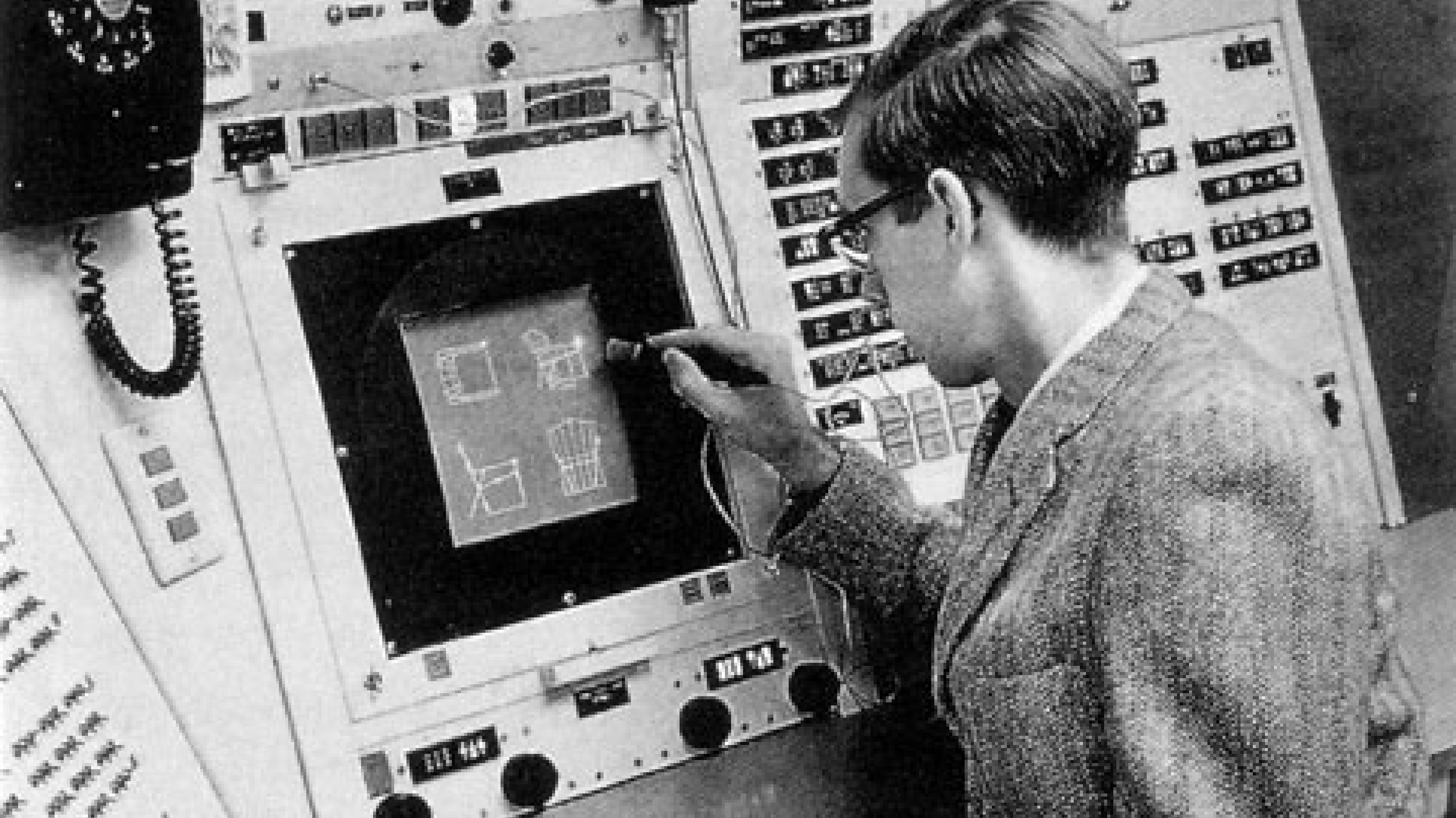

These early developments established fundamental principles still used today in modern rendering.
1980s: CGI Revolution
- 1982: "Tron" becomes first film with extensive CGI sequences
- 1984: Development of ray tracing algorithms by Turner Whitted
- 1986: Pixar releases "Luxo Jr." - first fully CGI-animated film nominated for an Academy Award
- 1989: Introduction of Photoshop 1.0, revolutionizing digital image manipulation

1990s: The Software Revolution
This decade witnessed an explosion in professional 3D software development:
-
Autodesk Maya (1998)
- Industry-leading animation tools
- Advanced character rigging system
- MEL scripting language for customization
- Pioneering particle systems and dynamics
-
Cinema 4D Evolution
- 1990: Initial release as ray-tracer for Amiga
- 1993: Introduction of animation capabilities
- 1996: Windows version released
- 1997: MoGraph module revolutionizes motion graphics
-
3ds Max Development
- Originally released as 3D Studio DOS in 1990
- 1996: Rebranded as 3D Studio MAX
- Key features:
- Advanced modeling tools
- Character animation system
- Architectural visualization capabilities
- Plugin architecture
As noted by John Lasseter, Pixar co-founder: "The art challenges technology, and technology inspires the art." This symbiotic relationship defined the rapid advancement of 3D software during the 1990s.
Modern 3D Rendering Software
Software Behind Blockbusters
| Studio | Core Software | Specialized Tools | Notable Implementations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marvel Studios | Maya, Houdini | Custom VFX Suite, Nuke | Thanos digital double in "Avengers: Endgame" |
| Pixar Animation | RenderMan, Maya | Presto Animation System | Water simulation in "Finding Nemo" |
| Industrial Light & Magic | Maya, Houdini | Zeno Framework | Real-time LED wall tech for "The Mandalorian" |
| Weta Digital | Maya, Massive | Proprietary Physics Engine | Motion capture in "Avatar" |
Detailed Software Implementation
-
Marvel Studios Workflow
- Primary Pipeline:
- Maya: Character rigging with custom muscle system
- Houdini: Environmental destruction and particle effects
- Nuke: Multi-pass compositing with AI-enhanced workflows
- Custom Solutions:
- Proprietary asset management system
- Real-time preview renderer
- Cloud-based collaboration tools
- Primary Pipeline:
-
Pixar's Technical Excellence
"RenderMan wasn't just built for speed - it was built for artistic freedom." - Ed Catmull, Pixar Co-founder
- RenderMan Capabilities:
- Path-traced global illumination
- Advanced subsurface scattering
- Neural network denoising
- Presto Animation System:
- Non-destructive animation layers
- Real-time character previews
- Automated crowd systems
- RenderMan Capabilities:
-
ILM's Technical Innovation
- Proprietary Tools:
- Zeno: Unified production framework
- ReactorCore: Physics simulation engine
- Block Party: Asset management system
Their StageCraft virtual production system revolutionized filming with real-time rendered backgrounds, using:
- Unreal Engine integration
- Custom camera tracking
- LED wall synchronization
- Dynamic lighting adaptation
- Proprietary Tools:
-
Weta Digital's Advanced Systems
- Specialized Software:
- Massive: AI-driven crowd simulation
- Tissue: Anatomically correct muscle system
- Manuka: Physics-based renderer
- Specialized Software:
The AI Revolution in 3D Rendering
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing the 3D rendering landscape, introducing groundbreaking technologies that are reshaping the industry:
Next-Generation AI Technologies in Rendering
| Technology | Applications | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Generative AI | Asset creation, scene composition | 90% reduction in initial modeling time |
| Gaussian Splatting | Real-time neural rendering | 10x faster than traditional methods |
| Diffusion Models | Texture generation, style transfer | Photorealistic material creation in minutes |
| Neural Radiance Fields | Volume rendering, scene reconstruction | Revolutionary 3D scene capture from 2D images |
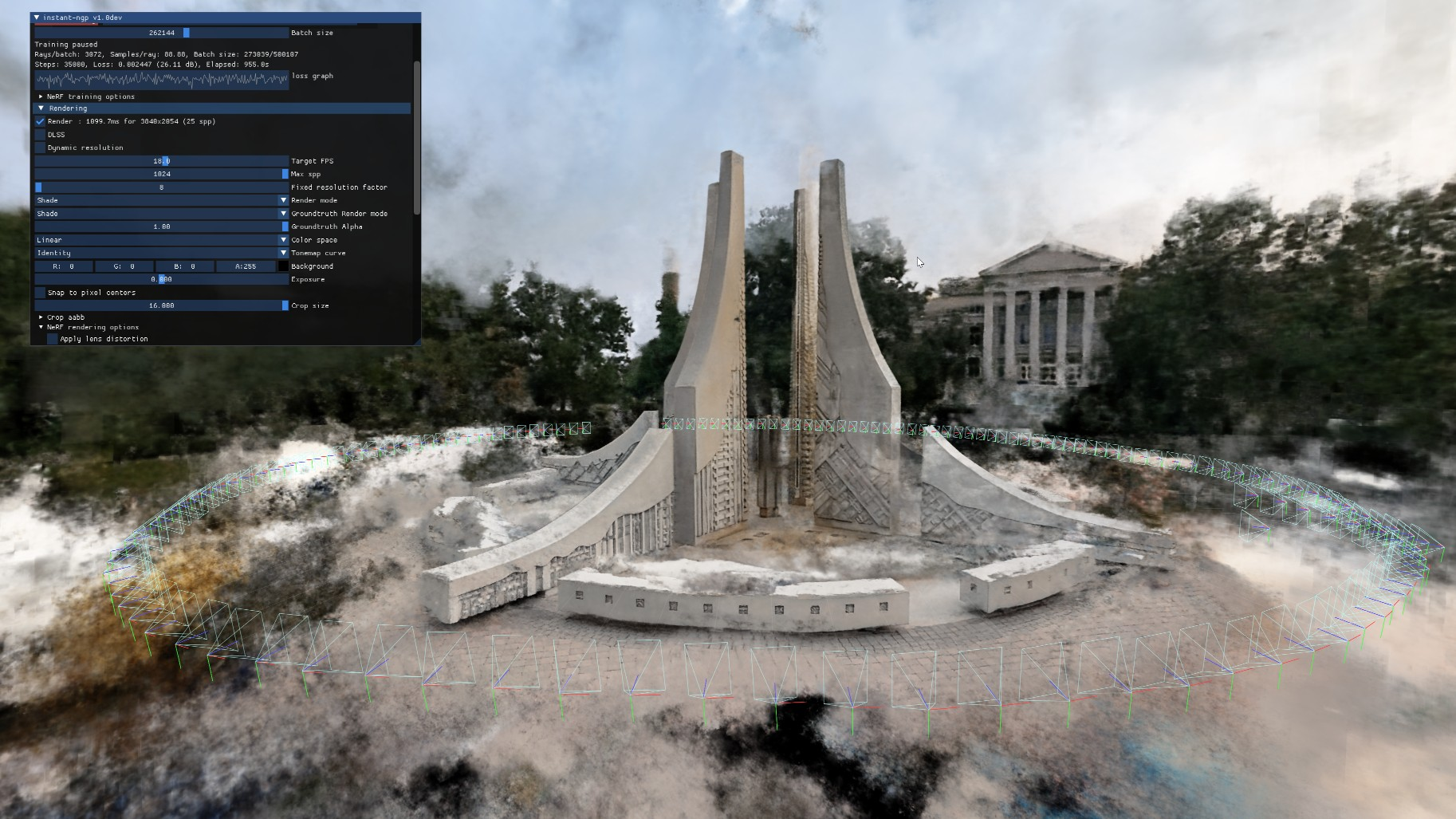
Core AI-Powered Innovations
- Intelligent Denoising Systems
- NVIDIA OptiX AI Denoiser: 500x faster than traditional denoising
- Intel Open Image Denoise: Advanced temporal stability
- AMD FidelityFX Denoiser: Real-time ray tracing enhancement
- Advanced Neural Networks
- Automated UV Unwrapping: 99.9% accuracy in texture mapping
- Smart Material Generation: PBR-compliant material creation
- Pose Estimation: 200+ joint tracking points
"The integration of diffusion models in 3D rendering pipelines has reduced the asset creation time by 85% while maintaining unprecedented quality levels." - Jensen Huang, NVIDIA CEO
Emerging AI Technologies
- Gaussian Splatting Innovations
- 3D Scene Reconstruction: Instant photorealistic results
- Dynamic Resolution Scaling: Adaptive quality based on viewpoint
- Memory Efficiency: 70% reduction in storage requirements
- Diffusion Model Applications
- Texture Synthesis: Generate PBR textures from text prompts
- Style Transfer: Real-time material appearance modification
- Asset Generation: Create complex 3D models from descriptions
Quantifiable Benefits
| Metric | Traditional Pipeline | AI-Enhanced Pipeline | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Render Time | 24 hours | 2.4 hours | 90% |
| Asset Creation | 1 week | 1 day | 86% |
| Iteration Speed | 4 hours | 15 minutes | 94% |
| Cost Savings | Baseline | Reduced by 75% | 75% |
Democratization Through AI
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing 3D rendering by making it accessible to everyone, not just professionals. This transformation is breaking down traditional barriers to entry and enabling new creative possibilities.
Simplified Creation
AI-powered tools now allow complete beginners to create 3D models and scenes through simple text prompts or rough sketches. What once required years of technical expertise can now be accomplished in minutes.
Automated Optimization
Smart AI systems automatically handle complex technical aspects like topology, UV mapping, and optimization, eliminating the need for deep technical knowledge.
Impact on Different Users
- Hobbyists: Create professional-quality 3D art without expensive software or training
- Small Businesses: Produce marketing materials and product visualizations at a fraction of the cost
- Content Creators: Generate 3D assets for social media and online content instantly
- Students: Learn and experiment with 3D creation without technical barriers
Current Limitations
While AI has made 3D creation more accessible, some challenges remain:
- Control and Customization: AI-generated results may need fine-tuning for specific needs
- Internet Dependency: Most AI tools require stable internet connection
- Quality Consistency: Results can vary based on prompt clarity and AI model capabilities
- Creative Boundaries: AI models are limited by their training data
Conclusion
3D rendering has come a long way from its humble beginnings, evolving into a sophisticated technology that combines artistry with technical expertise. The integration of AI is pushing the boundaries of what's possible, making high-quality 3D rendering more accessible and efficient than ever before.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments in the field of 3D rendering, further transforming how we create and visualize digital content across industries.